We have to print the data of nodes of the linked list at the given index. Unlike array linked list generally don’t have index so we have to traverse the whole linked list and print the data when we reached a particular.
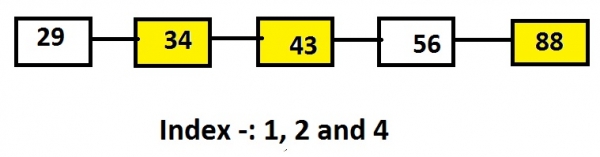
Let’s say, list contains the nodes 29, 34, 43, 56 and 88 and the value of indexes are 1, 2 and 4 than the output will be the nodes at these indexes that are 34, 43 and 88.
Example
Linked list: 29->34->43->56->88 Input: 1 2 4 Output: 34 43 88
In above representation of Linked List the yellow highlighted nodes are the nodes to be printed or the nodes which are on a particular index.
The approach used here involves taking of one pointer and one counter variable initialised to 1 that will incremented whenever the node is traversed. The counter is matched with the key value. When the key matches with the counter value the pointer pointing to the node structure will print the node’s data and incremented to next node and so on giving us the nodes at particular key.
The below code shows the c implementation of the algorithm given.
Algorithm
START
Step 1 -> create node variable of type structure
Declare int data
Declare pointer of type node using *next
Step 2 -> create struct node* intoList(int data)
Create newnode using malloc
Set newnode->data = data
newnode->next = NULL
return newnode
step 3 -> Declare function void displayList(struct node *catchead)
create struct node *temp
IF catchead = NULL
Print list is empty
return
End
Set temp = catchead
Loop While (temp != NULL)
print temp->data
set temp = temp->next
End
Step 4 -> Declare Function int search(int key,struct node *head)
Set int index
Create struct node *newnode
Set index = 0 and newnode = head
Loop While (newnode != NULL & newnode->data != key)
Set index++
Set newnode = newnode->next
End
return (newnode != NULL) ? index : -1
step 5 -> In Main()
create node using struct node* head = intoList(9)
call displayList(head)
set index = search(24,head)
IF (index >= 0)
Print index
Else
Print not found in the list
EndIF
STOPExample
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
//structure of a node
struct node {
int data;
struct node *next;
};
struct node* intoList(int data) {
struct node* newnode = (struct node*)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
newnode->data = data;
newnode->next = NULL;
return newnode;
}
//funtion to display list
void displayList(struct node *catchead) {
struct node *temp;
if (catchead == NULL) {
printf("List is empty.");
return;
}
printf("elements of list are : ");
temp = catchead;
while (temp != NULL) {
printf("%d ", temp->data);
temp = temp->next;
}
printf("
");
}
//function to search element
int search(int key,struct node *head) {
int index;
struct node *newnode;
index = 0;
newnode = head;
while (newnode != NULL && newnode->data != key) {
index++;
newnode = newnode->next;
}
return (newnode != NULL) ? index : -1;
}
int main() {
int index;
struct node* head = intoList(9); //inserting elements into a list
head->next = intoList(76);
head->next->next = intoList(13);
head->next->next->next = intoList(24);
head->next->next->next->next = intoList(55);
head->next->next->next->next->next = intoList(109);
displayList(head);
index = search(24,head);
if (index >= 0)
printf("%d found at position %d
", 24, index);
else
printf("%d not found in the list.
", 24);
index=search(55,head);
if (index >= 0)
printf("%d found at position %d
", 55, index);
else
printf("%d not found in the list.
", 55);
}
输出
如果我们运行上面的程序,它将生成以下输出。
elements of list are : 9 76 13 24 55 109 24 found at position 3 55 found at position 4



